 IATF 16949 training is designed to help organizations in the automotive industry understand and implement the requirements of the IATF 16949 standard, which is the globally recognized quality management system standard for automotive manufacturing. The training typically includes the following components:
IATF 16949 training is designed to help organizations in the automotive industry understand and implement the requirements of the IATF 16949 standard, which is the globally recognized quality management system standard for automotive manufacturing. The training typically includes the following components:
1. Introduction to IATF 16949
Overview of the IATF 16949 standard and its purpose.Understanding the history and evolution of the standard.
Key differences between IATF 16949 and other quality management standards, such as ISO 9001.
2. Quality Management System Requirements
Detailed explanation of the IATF 16949 requirements, including context of the organization, leadership, planning, support, operation, performance evaluation, and improvement.Specific automotive industry requirements and how they differ from general quality management systems.
Risk-based thinking and the importance of identifying and mitigating risks in automotive manufacturing.

 AI can play a significant role in implementing and maintaining an IATF 16949 quality management system (QMS). Here are several ways AI can assist in this process:
AI can play a significant role in implementing and maintaining an IATF 16949 quality management system (QMS). Here are several ways AI can assist in this process: The perception of IATF 16949 auditors by employees can vary depending on various factors such as the auditor's demeanor, communication skills, and the overall audit process. Here are some common perceptions that employees may have regarding IATF 16949 audit and what you can do to promote the benefits:
The perception of IATF 16949 auditors by employees can vary depending on various factors such as the auditor's demeanor, communication skills, and the overall audit process. Here are some common perceptions that employees may have regarding IATF 16949 audit and what you can do to promote the benefits: An auto strike can have several impacts on the implementation of the IATF 16949 standard, which is a specific quality management system standard designed for the automotive industry. The extent of these impacts can vary depending on the duration and severity of the strike, as well as the specific circumstances of the organization. Here are some ways in which an auto strike can affect IATF 16949 implementation:
An auto strike can have several impacts on the implementation of the IATF 16949 standard, which is a specific quality management system standard designed for the automotive industry. The extent of these impacts can vary depending on the duration and severity of the strike, as well as the specific circumstances of the organization. Here are some ways in which an auto strike can affect IATF 16949 implementation: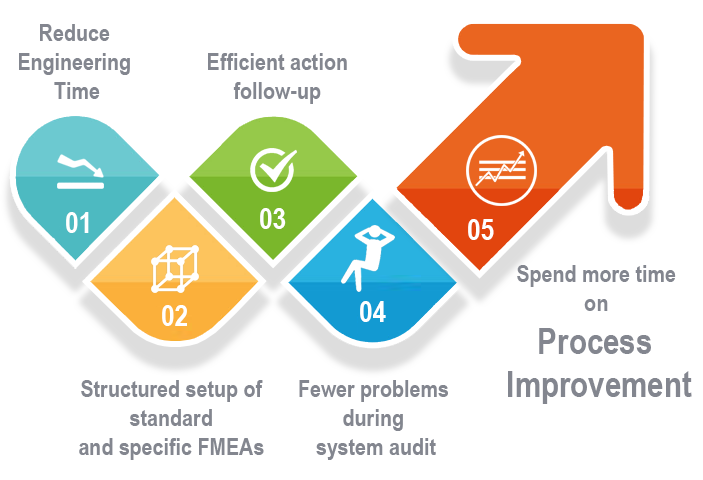 Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a step-by-step approach for identifying all possible failures in a design, manufacturing or assembly process, or a product or service. It is a structured approach to discovering potential failures that may exist within the design of a product or process.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a step-by-step approach for identifying all possible failures in a design, manufacturing or assembly process, or a product or service. It is a structured approach to discovering potential failures that may exist within the design of a product or process.