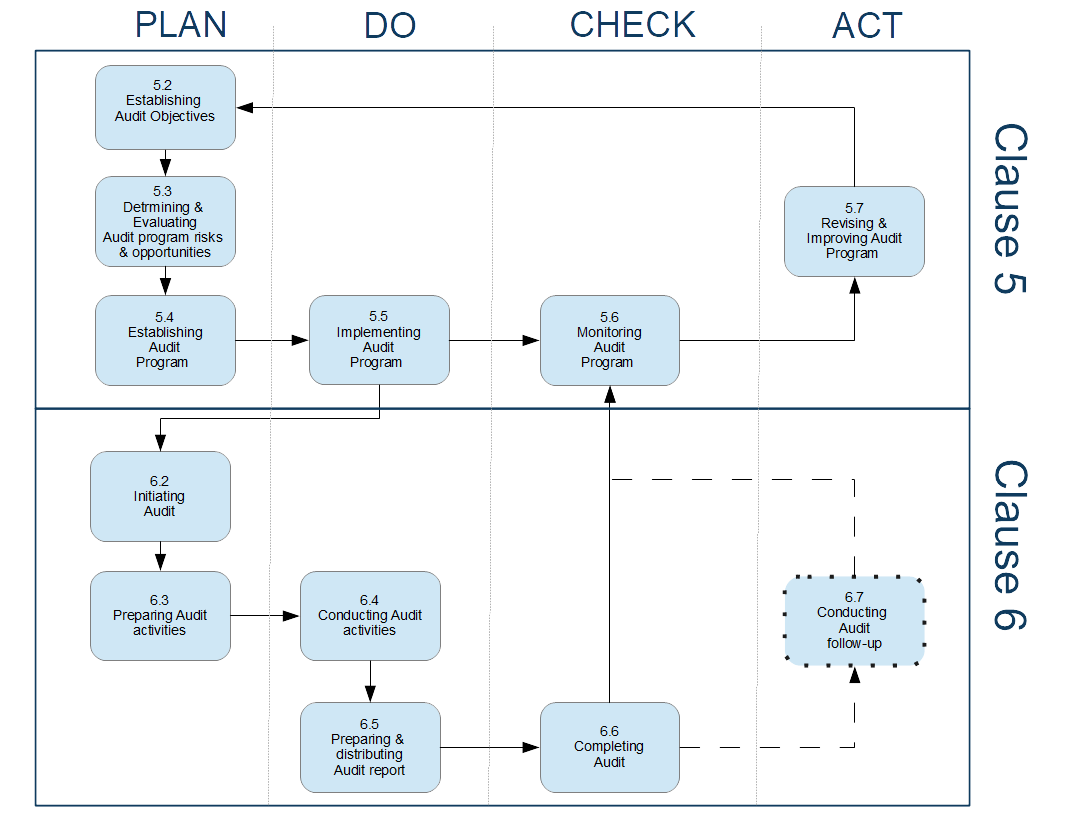
 Click Image for a Larger ViewThe Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle is the cornerstone of the ISO standards. The ISO 19011 standard describes how organizations perform audits. It is designed to ensure that audits are conducted systematically, consistently, and are continuously improved.
Click Image for a Larger ViewThe Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle is the cornerstone of the ISO standards. The ISO 19011 standard describes how organizations perform audits. It is designed to ensure that audits are conducted systematically, consistently, and are continuously improved.
This cycle is a core part of ISO management systems and applies to the management of an audit program as well. Here is a short description of the cycle:
Plan
- Define Objectives: Establish the objectives and scope of the audit program to ensure it supports the organization’s policies, objectives, and performance.
- Determine Resources: Identify and allocate the necessary resources for the audit program, including personnel, tools, and time.
- Schedule Audits: Plan the audit schedule based on the risk and importance of the processes to be audited.
- Develop Audit Plan: Each individual audit should have a plan that outlines its scope, criteria, duration, and resources required.
Do
- Conduct Audits: Execute the audits according to the audit plan, using appropriate techniques to collect and verify information.
- Gather Evidence: Collect audit evidence that is relevant, sufficient, and objective to support audit findings and conclusions.
- Report Findings: Document the audit findings, including any non-conformities, and report them to the relevant management.
Check
- Review Audit Results: Evaluate the audit findings and the effectiveness of the audit program against its objectives.
- Management Review: Present the audit outcomes to top management for review, including the effectiveness of the organization’s management system and any need for improvements.
Act
- Implement Improvements: Take corrective and preventive actions based on the audit findings to address non-conformities and improve the management system.
- Update Audit Program: Based on the results and feedback from the audits, update the audit program to reflect changes in risks, processes, and organizational objectives.
- Continual Improvement: Use the insights gained from the audits to drive continual improvement of the audit process and the management system as a whole.
To learn more take this short, cost effective ISO 19011 course.
